Tugboat engines typically produce 500 to 2,500 kW (~ 680 to 3,400 hp), but larger boats (used in deep waters) can have power ratings up to 20,000 kW (~ 27,200 hp) and usually have an extreme power: tonnage-ratio (normal cargo and passenger ships have a P: T-ratio (in kW: GRT) of 0.35 to 1.20, whereas large tugs typically are 2.20 to 4.50 and small harbour-tugs 4.0 to 9.5). The engines are often the same as those used in railroad locomotives, but typically drive the propeller mechanically instead of converting the engine output to power electric motors, as is common for diesel-electric locomotives. For safety, tugboats' engines often feature two of each critical part for redundancy.
Tugboats are highly maneuverable. Kort nozzles are added to increase thrust per kW/hp. This was followed by the nozzle-rudder, which omitted the need for a conventional rudder. The cycloidal propeller was developed prior to World War II and was occasionally used in tugs because of its maneuverability. After WWII it was also linked to safety due to the development of the Voith Water Tractor, a tugboat configuration which could not be pulled over by its tow. These propulsion systems are used on tugboats designed for tasks such as ship docking and marine construction. Conventional propeller/rudder configurations are more efficient for port-to-port towing.
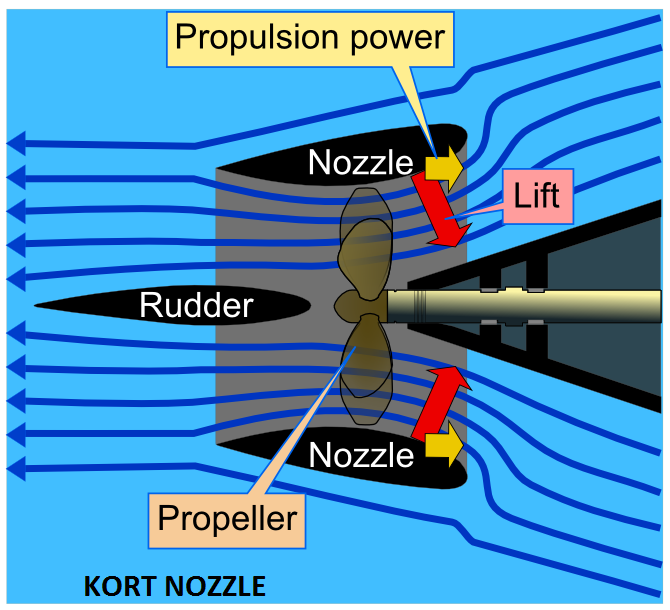
The Kort nozzle is a sturdy cylindrical structure around a special propeller having minimum clearance between the propeller blades and the inner wall of the Kort nozzle. The thrust: power ratio is enhanced because the water approaches the propeller in a linear configuration and exits the nozzle the same way. The Kort nozzle is named after its inventor, but many brands exist.
A recent Dutch innovation is the Carousel Tug, winner of the Maritime Innovation Award at the Dutch Maritime Innovation Awards Gala in 2006.[6] The Carousel Tug adds a pair of interlocking rings to the body of the tug, the inner ring attached to the boat, with the outer ring attached to the towed ship by winch or towing hook. Since the towing point rotates freely, the tug is very difficult to capsize.[7]
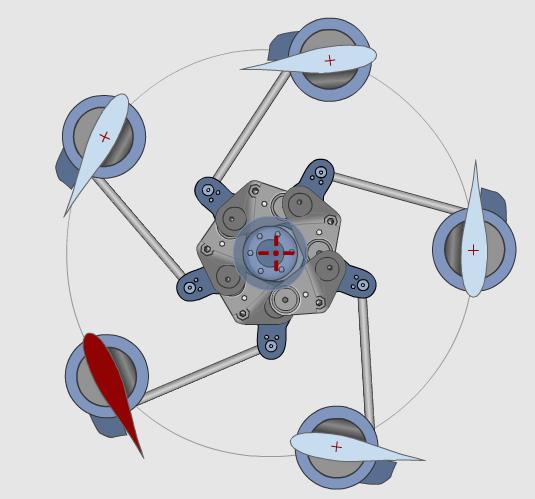
The Voith Schneider propeller (VSP), also known as a cycloidal drive is a specialized marine propulsion system. It is highly maneuverable, being able to change the direction of its thrust almost instantaneously. It is widely used on tugs and ferries.
From a circular plate, rotating around a vertical axis, a circular array of vertical blades (in the shape of hydrofoils) protrudes out of the bottom of the ship. Each blade can rotate itself around a vertical axis. The internal gear changes the angle of attack of the blades in sync with the rotation of the plate, so that each blade can provide thrust in any direction, very similar to the collective pitch control and cyclic in a helicopter.
Tugboats are highly maneuverable. Kort nozzles are added to increase thrust per kW/hp. This was followed by the nozzle-rudder, which omitted the need for a conventional rudder. The cycloidal propeller was developed prior to World War II and was occasionally used in tugs because of its maneuverability. After WWII it was also linked to safety due to the development of the Voith Water Tractor, a tugboat configuration which could not be pulled over by its tow. These propulsion systems are used on tugboats designed for tasks such as ship docking and marine construction. Conventional propeller/rudder configurations are more efficient for port-to-port towing.
The Kort nozzle is a sturdy cylindrical structure around a special propeller having minimum clearance between the propeller blades and the inner wall of the Kort nozzle. The thrust: power ratio is enhanced because the water approaches the propeller in a linear configuration and exits the nozzle the same way. The Kort nozzle is named after its inventor, but many brands exist.
A recent Dutch innovation is the Carousel Tug, winner of the Maritime Innovation Award at the Dutch Maritime Innovation Awards Gala in 2006.[6] The Carousel Tug adds a pair of interlocking rings to the body of the tug, the inner ring attached to the boat, with the outer ring attached to the towed ship by winch or towing hook. Since the towing point rotates freely, the tug is very difficult to capsize.[7]
The Voith Schneider propeller (VSP), also known as a cycloidal drive is a specialized marine propulsion system. It is highly maneuverable, being able to change the direction of its thrust almost instantaneously. It is widely used on tugs and ferries.
From a circular plate, rotating around a vertical axis, a circular array of vertical blades (in the shape of hydrofoils) protrudes out of the bottom of the ship. Each blade can rotate itself around a vertical axis. The internal gear changes the angle of attack of the blades in sync with the rotation of the plate, so that each blade can provide thrust in any direction, very similar to the collective pitch control and cyclic in a helicopter.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed